Integrating PRINCE2 and Scrum
In the world of project management, professionals often seek methodologies that can optimize processes and enhance product delivery. Two popular frameworks are PRINCE2 and Scrum. While each has its strengths, there is an ongoing discussion about whether they can be effectively combined to leverage the benefits of both structured planning and agile adaptability.
Understanding PRINCE2
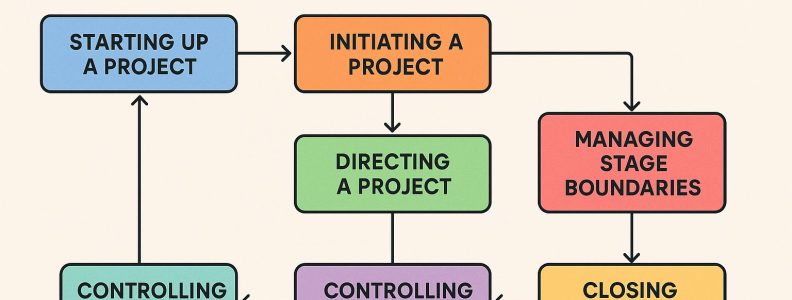
PRINCE2, standing for Projects IN Controlled Environments, is a process-based method specifically designed for project management. This framework is characterized by its emphasis on control and organization. PRINCE2 segments projects into distinct phases with clearly outlined objectives and deliverables, facilitating high predictability and control over outcomes. The detailed guidance provided by PRINCE2 is tailored to environments demanding consistency and reliability, such as governmental projects or large-scale industrial endeavors.
Benefits of PRINCE2
The advantages of using PRINCE2 lie in its robust framework, which comprises explicit stages. This modularity aids in meticulous risk management and ensures consistency across the lifecycle of a project. Moreover, PRINCE2 encourages a regime of frequent reviews that assess progress against predefined plans and business cases. This methodical review process ensures projects remain aligned with overarching business objectives, thereby safeguarding stakeholder interests and organizational goals.
The Scrum Framework
On the other hand, Scrum emerges as a pioneer in the landscape of agile methodologies, predominantly aimed at the sector of software development, yet its principles have become adaptable across various industries. Scrum promotes iterative progress through time-boxed segments known as sprints. This approach fosters an environment of teamwork, adaptability, and rapid delivery, contrasting sharply with the regimented philosophy of PRINCE2.
Advantages of Scrum
Scrum’s strength is its facilitation of adaptability and rapid decision-making, which allows teams to react swiftly to changing requirements or unforeseen challenges. By incorporating daily stand-ups, or short meetings to synchronize team activities, Scrum enhances communication and emphasizes the delivery of working products, often at the expense of intensive documentation. This prioritization ensures that projects remain focused on the results.
Can PRINCE2 and Scrum Coexist?
The exploration of integrating PRINCE2 and Scrum is driven by the desire to harness the strategic strengths of both frameworks. While PRINCE2 offers a foundational governance structure, Scrum contributes by enhancing team synergy and responsiveness. The integration of these methodologies aims to provide a more comprehensive approach to project management.
Aligning PRINCE2 and Scrum Principles
Successfully combining these frameworks requires a thoughtful alignment of PRINCE2’s stages with the iterative nature of Scrum cycles. The assurance roles specified in PRINCE2 can complement Scrum teams by ensuring that robust governance methods are applied without impeding the agile process. A strategically balanced integration might involve:
– Employing PRINCE2’s comprehensive framework to define and plan projects at a strategic level while using Scrum’s agile processes for hands-on execution.
– Leveraging Scrum’s iterative sprints to deliver tangible outputs from the strategic plans governed by PRINCE2.
– Implementing PRINCE2’s rigorous risk management techniques in tandem with Scrum’s inherent adaptability, enhancing the overall resilience of project management strategies.
Challenges of Integration
Integrating PRINCE2 and Scrum presents its own unique set of challenges, primarily due to their inherent philosophical differences. PRINCE2’s structured and rigid approach may sometimes seem at odds with Scrum’s fluid and adaptive nature, creating potential friction points when attempting to combine the two. A successful integration necessitates a custom approach, adapting certain elements from each methodology to complement the other effectively, rather than striving for a perfect synthesis.
Conclusion
The integration of PRINCE2 with Scrum can prove beneficial, offering organizations a robust project management solution that combines the meticulous governance and structure of PRINCE2 with the flexibility and dynamism of Scrum. By intelligently harnessing both methodologies, project teams can achieve a balance that leads to successful project delivery. However, this requires meticulous planning, innovative adaptation, and effective communication to navigate and resolve potential challenges that may arise in the integration journey. For further insights on effectively combining these methodologies, one can delve into expert analyses, case studies, and resources within the project management community.