Introduction to PRINCE2 Workflows
PRINCE2, an acronym for Projects IN Controlled Environments, is recognized worldwide as a robust framework for project management. It emphasizes organized management of projects through well-defined workflows that allow project managers to exercise control, thereby facilitating successful project outcomes. This article delves into how PRINCE2 workflows interact across various processes to create a cohesive project management strategy.
Overview of PRINCE2 Processes
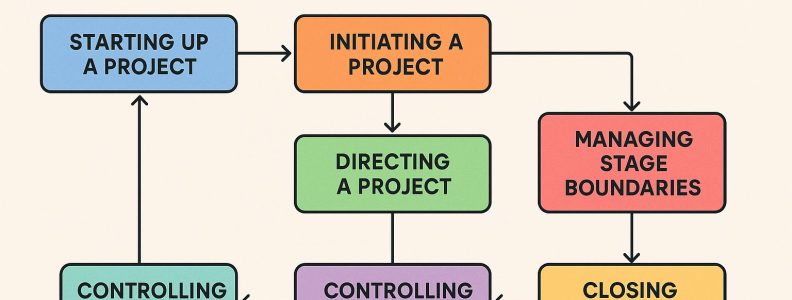
The PRINCE2 methodology is structured around several fundamental processes integral to guiding a project from its inception to closure. These processes are systematically outlined to provide a strong framework for effective project management. Major processes within PRINCE2 include:
Starting Up a Project (SU): This is the project’s foundational phase. Here, steps are taken to ensure that the project board fully grasps the project’s feasibility and its alignment with the overarching business case. The board makes preliminary decisions that shape the project’s direction and strategy.
Directing a Project (DP): This process delineates the role of the project board, emphasizing its strategic oversight responsibilities. The board remains detached from day-to-day project activities, focusing instead on high-level decisions and steering the project strategically.
Initiating a Project (IP): During this phase, detailed groundwork for project governance is laid out with the preparation of comprehensive project initiation documentation. This establishes the performance framework and governance structure necessary for the project’s success.
Controlling a Stage (CS): In this process, managers handle routine project management tasks by continuously monitoring and controlling each project stage to keep alignment with the overarching project plans.
Managing Product Delivery (MP): This process focuses on ensuring project deliverables meet the predefined quality standards. It involves the generation, verification, and approval of outputs by project stakeholders.
Managing a Stage Boundary (SB): At this juncture, the current project stage’s achievements are evaluated and plans for the subsequent stage are drafted. This assessment maintains consistent alignment with the strategic directives of the project board.
Closing a Project (CP): In the concluding phase, the project’s tasks are wrapped up, deliverables are signed off, and crucial’s lessons are documented. Complete and timely communication of project closure is ensured.
Interaction Among Processes
The effective interaction of these processes is pivotal to achieving cohesive project management under the PRINCE2 system. Each process interconnects strategically to serve a specific function within the overall project framework.
Starting Up a Project and Initiating a Project: Following the preparation of the project mandate, initiation documentation is developed. This paperwork is indispensable for obtaining the necessary project board authorization and serves as a reference point throughout the project lifespan, guiding its trajectory.
Directing a Project and Controlling a Stage: Through the project’s life, the project board stays closely engaged, supplying paramount direction to ensure that the project remains consistent with the predetermined business objectives and the agreed-upon strategy.
Managing Product Delivery and Managing a Stage Boundary: The emphasis during product delivery is on realizing outputs as per the quality benchmarks, while the management of a stage boundary focuses on evaluating stages, reassessing risks, and forwarding necessary information to the project board for authorizing future stages.
Closure and Evaluation: In the project’s final stages, activities are methodically wrapped up, and all deliverables are assessed and accepted by the stakeholders. This transition period—from delivery to evaluation—plays a vital role in confirming that the project objectives have been successfully accomplished.
Conclusion
A thorough understanding of how PRINCE2 processes interact is crucial for effective project management. These interactions ensure that each aspect of the project aligns with strategic goals and deliverables consistently meet set quality standards and stakeholder satisfaction. Although each process is tasked with a unique function, their concerted interactions create a versatile yet controlled environment—a central trait of the PRINCE2 methodology. For those seeking more comprehensive guidance on implementing PRINCE2, it would be beneficial to explore resources provided by AXELOS, the organization responsible for developing and maintaining the PRINCE2 framework.
Through practical application and mastery of these processes and their interactions, project managers can achieve an enhanced level of control and adaptability. This results in accomplished projects that satisfy all stakeholder requirements while remaining within the defined constraints of scope, cost, and time.
Studying each phase of the project through the lens of these processes equips project managers with the skills required to dissect and address specific challenges that arise. This fosters an environment where decisions are made based on data and proven methodologies rather than conjecture and assumption.
Furthermore, the PRINCE2 methodology is distinguished by its flexibility, allowing it to be adapted to suit various project sizes and types. Whether managing a small-scale project or a large, complex initiative, the methodology’s foundational processes provide a valuable compass for navigation and decision-making.
The emphasis on iterative learning and adaptation ensures that each project under the PRINCE2 umbrella becomes a source of valuable insights, effectively feeding into a cycle of continuous improvement. By carefully documenting lessons learned and integrating them into future project strategies, organizations can refine their project management practices, improving outcomes progressively.
In conclusion, understanding PRINCE2 workflows and their interactions is not just about following a structured process; it is about fostering an environment where all project elements seamlessly align with overarching objectives, and stakeholders’ expectations are consistently exceeded. Through dedicated application and an insightful grasp of the methodology, project managers can not only lead successful projects but contribute to the sustained success and growth of their organizations.