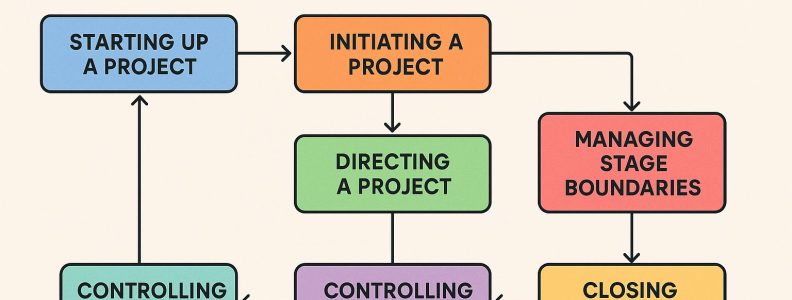
Understanding the PRINCE2 Change Control Approach
The PRINCE2 methodology, an acronym for Projects in Controlled Environments, is a globally acknowledged framework for project management. It provides a structured approach that emphasizes various aspects of project execution, with change control being a critical component. Ensuring that changes are managed systematically helps in minimizing risks and optimizing the benefits, thereby keeping the project on its intended path.
Why Change Control is Essential
Change is a common occurrence in projects, driven by internal insights or external factors. Any modification in a project has the potential to impact its scope, cost, timeline, and ultimately its success. The PRINCE2 framework introduces a structured approach to handle these changes, ensuring they contribute positively towards the project objectives instead of causing disruptions. This systematic method involves evaluating each change request meticulously to ensure it aligns with the project’s overall goals.
Key Components of PRINCE2 Change Control
Change Authority: One of the crucial elements of the PRINCE2 change control process is the establishment of a Change Authority. This could be an individual or a group assigned with the authority to approve changes within the project. Having a designated authority expedites decision-making processes while maintaining consistency in handling change requests.
Change Budget: PRINCE2 provides for a dedicated budget specifically for managing and implementing changes. By allocating funds for potential changes, projects can address necessary adjustments without compromising the entire project’s budget or resources, thus ensuring that the financial strain of changes is minimized.
Issue and Change Control Procedure: Another essential component is the comprehensive issue and change control procedure, which outlines the specific steps required to log, evaluate, and decide on changes. By following a clear procedure, the team ensures that changes are managed systematically and effectively, facilitating efficient resolution of issues.
Steps in the Change Control Process
PRINCE2 defines an explicit process for managing changes, which includes several critical steps to handle modifications efficiently:
Log the Request: When a change request is introduced, it first needs to be documented in the change log. This log must contain vital details about the nature of the change, its potential impact, and the identity of the individual or entity that requested it.
Impact Assessment: Following logging, the change request undergoes a detailed impact assessment. This evaluation is crucial as it examines the potential effects of the change on the project’s outcomes, timeline, resources, and overall viability.
Decision Making: Post-assessment, the next step is decision making. Here, the Change Authority reviews the analyses and decides whether to approve, reject, or defer the proposed change. The decision hinges on whether the change aligns with project objectives and how it affects the entire project framework.
Implementation: Once a change is approved, the implementation phase begins by updating the project plan accordingly. This stage is vital to ensure that changes are integrated smoothly without causing any unintended disruptions or delays in project execution.
Conclusion
Adopting a structured change control process, as advocated by PRINCE2, is integral for maintaining the stability and strategic direction of a project. By implementing this approach, project managers are better equipped to ensure that any changes introduced are both beneficial and well-managed. The alignment of changes with the project’s strategic goals helps in achieving project success without unnecessary setbacks. For those seeking a more in-depth understanding of PRINCE2, exploring official sources and comprehensive training materials can offer valuable insights and guidance on effective project management practices.
Implementing PRINCE2’s change control approach ensures that projects remain flexible enough to adapt to necessary changes while maintaining their focus and ensuring that strategic objectives remain at the forefront. This methodology, although primarily focused on change management, offers a structured framework that can be adapted to the broader aspects of project management, ensuring comprehensive handling of project-related challenges.